Utils Module
Features
This module provides the following Angular declarations that are useful for the definition of your documents:
- Angular pipes that can be used to format the display of value on your components,
- Directives that can be used to control the user interaction with your components,
- The injection token
SCREEN_SIZE_RULESto override the component sizing rules based on window/screen size of the application. - The
UIService
Import
import { UtilsModule, SCREEN_SIZE_RULES } from '@sinequa/components/utils';
/* If you want to change the screen size rules provided by @sinequa/components */
export const myScreenSizeRules = {
xl: "(min-width: 1650px)",
lg: "(min-width: 1400px) and (max-width: 1649.98px)",
md: "(min-width: 992px) and (max-width: 1399.98px)",
sm: "(min-width: 576px) and (max-width: 991.98px)",
xs: "(max-width: 575.98px)",
};
@NgModule({
imports: [
/*....*/
UtilsModule,
/*....*/
],
providers: [
/* If you want to change the screen size rules provided by @sinequa/components */
{ provide: SCREEN_SIZE_RULES, useValue: myScreenSizeRules },
/*....*/
],
/*....*/
})
API usage
Pipes
This modules provides the following Angular pipes
DatePipe
DatePipe provides the sqDate pipe that formats a Date object or a number of ticks (in number) to a localized date string.
Example:
<span>Date:</span><span style="color: red;">{{ new Date('2020-03-25') | sqDate }}</span>
yields (for English locale)
<span>Date:</span><span style="color: red;">03/25/2020</span>
This is equivalent as importing IntlService and calling IntlService.formatDate().
MomentPipe
If you use the moment.js library to manipulate date and time value instead of Date from javascript, you can use MomentPipe to format your moment values.
The pipe accepts a MomentParams to configure the formatting result:
format: The format of the result date, if this property is given, the pipe ignores the other properties,type: The type of value formatting, the valid values are:'iso': formats themomentobject as ISO-8601 date string, eg.'Tue Mar 24 2020 00:00:00 GMT+0100'=>'2020-03-23T23:00:00.000Z','unix': formats themomentobject as Unix timestamp (i.e. the number of seconds since the Unix Epoch - January 1 1970 12AM UTC), eg.'Tue Mar 24 2020 00:00:00 GMT+0100'=>'1585004400','valueOf'same as'unix'but the unit is in milliseconds, eg.'Tue Mar 24 2020 00:00:00 GMT+0100'=>'1585004400000','daysInMonth': formats themomentobject as the number of days in the given month, of the given year, eg.'Tue Feb 24 2020 00:00:00 GMT+0100'=>'29'or'Tue Feb 24 2019 00:00:00 GMT+0100'=>'28''fromNow': formats themomentobject as user-friendly relative time to the current time, which is also called timeago, eg.'Tue Jan 24 2020 00:00:00 GMT+0100'=>'2 months ago'(current time being Tue Mar 24 2020). seemoment.fromNow().'from': same as'fromNow'but you can specify the reference date (asmomentobject) usingreferenceproperty. seemoment.from().'toNow': same as'toNow'but in the opposite interval, one can think'toNow' === -'fromNow', eg.'Tue Jan 24 2020 00:00:00 GMT+0100'=>'in 2 months'(current time being Tue Mar 24 2020). seemoment.toNow().'to': same as'toNow'but you can specify specify the reference date (asmomentobject) usingreferenceproperty. seemoment.to().'calendar': displays time relative to a reference time (given by thereferenceobject, or default to current time). It is slightly different to'fromX'or'toX'in that the result string depends on how close to the reference time your value is, eg.'Tue Mar 22 2020 00:00:00 GMT+0100'=>'Last Sunday at 12:00 AM'(current time being Tue Mar 24 2020) or'Mon Mar 30 2020 00:00:00 GMT+0100'=>'Monday at 1:00 AM'(current time being Tue Mar 24 2020). seemoment.calendar().'diff': displays the time difference w.r.t. a reference time (given by thereferenceobject) in milliseconds, it has the same direction as'fromX', eg.'Tue Mar 22 2020 00:00:00 GMT+0100'with reference'Mon Mar 30 2020 00:00:00 GMT+0100'=>'-518400000'. seemoment.diff().
suffix: if false, a chronological suffix (i.e.'ago'or'in ...') is added to the result of'fromX'and'toX'. If true, a neutral time amount is returned, eg.'a months','two years'.reference: The reference date for the formatting of'from','to','calendar'and 'diff'unit: The time unit when formatting with'diff', eg.'hours','seconds'.precise: The'diff'formatting returns a rounded integer by default, if you want a floating-point number instead, put this property astrue.
<span>Moment:</span><span style="color: red;">{{ moment('1995-12-25') | sqMoment:{ type: 'fromNow', reference: moment('2015-12-25') } }}</span>
yields
<span>Moment:</span><span style="color: red;">24 years</span>
RelativeTimePipe
RelativeTimePipe provides the sqRelativeTime pipe that formats a number, specifying a date time relative to the current time, to a localized date time string.
This pipe is inspired from ECMA-402 RelativeTimeFormat Objects.
Example:
<span>Relative time:</span><span style="color: red;">{{ -7 | sqRelativeTime:{unit: 'days'} }}</span>
yields (in English locale)
<span>Relative time:</span><span style="color: red;">7 days ago</span>
This is equivalent as importing IntlService and calling IntlService.formatRelativeTime().
TimePipe
TimePipe provides the sqTime pipe that formats a Date object or a number of ticks (in number) to a localized time string.
Example:
<span>Time:</span><span style="color:red;">{{ new Date('2020-03-25 12:20:00.00Z') | sqTime }}</span>
yields (for English locale and UTC)
<span>Time:</span><span style="color:red;">12:20:00</span>
This is equivalent as importing IntlService and calling IntlService.formatTime().
MemorySizePipe
MemorySizePipe provides the sqMemorySize pipe that formats a file size in bytes a localized size string with the appropriate size unit (TB, GB, etc.).
Example:
<span>Size:</span><span style="color:red;">{{ 16384 | sqMemorySize }}</span>
yields (for English locale)
<span>Size:</span><span style="color:red;">16KB</span>
This is equivalent as importing FormatService and calling FormatService.formatMemorySize().
NumberPipe
NumberPipe provides the sqNumber pipe that formats a number to the locale format, i.e. using dot '.' as floating point for English and comma ',' for French.
Example:
<span>Decimal number:</span><span style="color:red;">{{ 3.14 | sqNumber }}</span>
yields (for French locale)
<span>Size:</span><span style="color:red;">3,14</span>
This is equivalent as importing IntlService and calling Intl.formatNumber().
ValuePipe
ValuePipe provides the sqValue pipe that formats a value coming from an index column based on the value type of that column.
Example:
<div>boolean:<span style="color:red;">{{ true | sqValue }}</span></div>
<div>number:<span style="color:red;">{{ 3.14 | sqValue }}</span></div>
yields (in French locale)
<div>boolean:<span style="color:red;">vrai</span></div>
<div>number:<span style="color:red;">3,14</span></div>
This is equivalent as importing FormatService and calling Intl.formatFieldValue().
ExprPipe
ExprPipe provides the sqExpr pipe that is mainly used to display a query filter.
You can see the usage of this pipe in the breadcrumbs or MySearch facet.
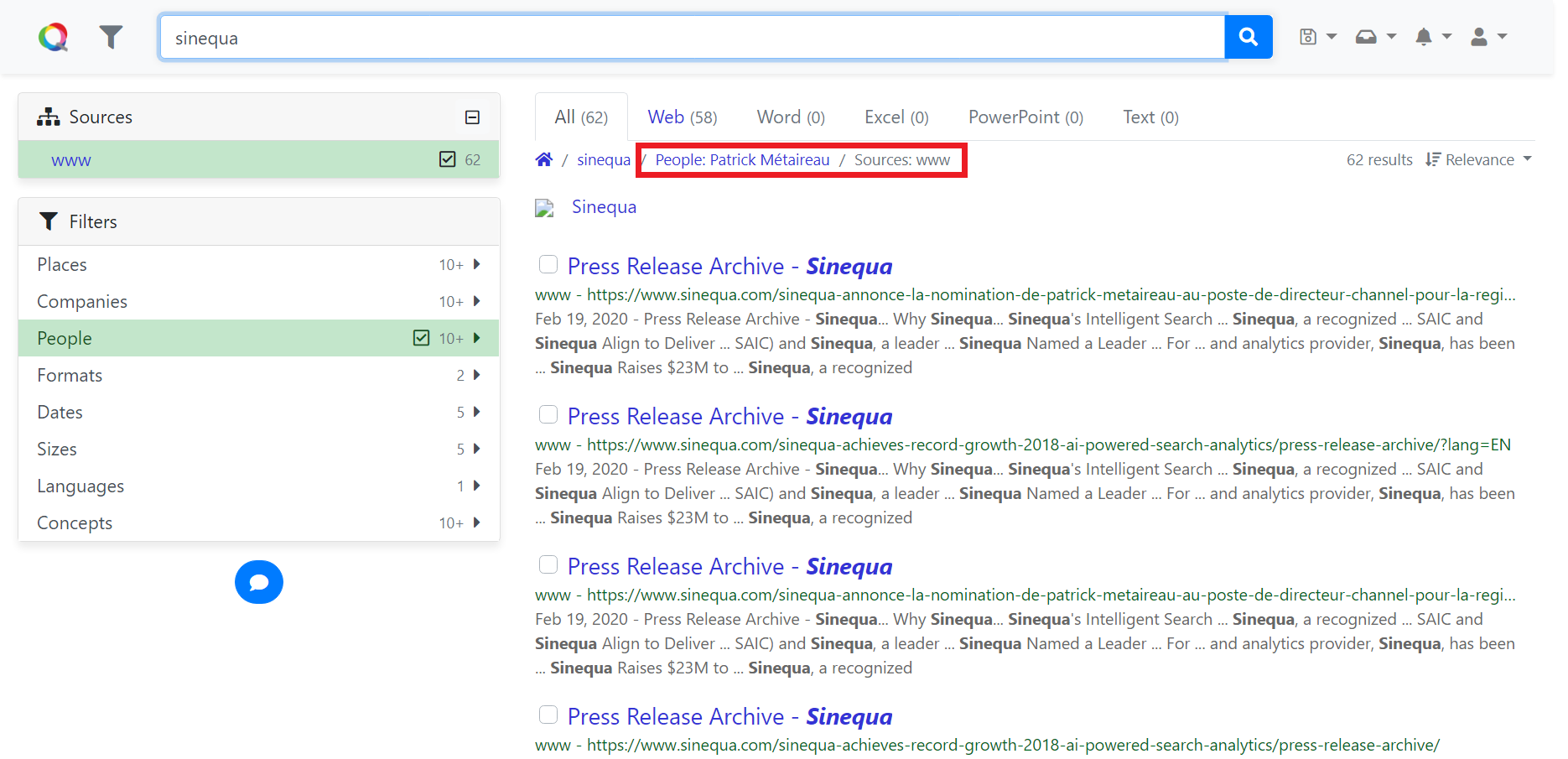 Filters displayed with ExprPipe in breadcrumbs
Filters displayed with ExprPipe in breadcrumbs
Example:
<span title="{{item.display | sqExpr:{withFields: displayFieldNames} }}"></span>
Directives
Autofocus directive
The sqAutofocus directive specifies which input component to be automatically focused when your component is opened.
Example:
<textarea
type="text"
class="form-control"
id="myInput"
sqAutofocus
>
ClickOutside directive
The sqClickOutside directive is a syntactic sugar
that helps you manage the behavior of your input component when user clicks outside the component area.
The input for this directive is a ClickOutsideOptions:
exclude: A list of HTML selectors for the HTML elements that will not be effected by this directive. If any HTML element not matching the HTML selectors but contains matching children HTML is also ignored by the directive.
When a user clicks outside of your component, the directive emits an click event via its output sqClickOutside.
By providing a callback to this output, you can act on the event.
Example:
<form name="myform" novalidate [formGroup]="form">
<sq-modal [title]="model.title" [buttons]="buttons">
<div class="form-group sq-form-group">
<label for="myInput">Input:</label>
<input
type="text"
class="sq-label-input"
(sqClickOutside)="clickOutside()"
name="myInput"
[(ngModel)]="myInputRef.value"
>
</div>
</sq-modal>
</form>
ScrollIntoView directive
The sqScrollIntoView directive is a syntactic sugar that helps to make sure a dynamically rendered child component of the current component to be in the visible area of the window.
This is useful when your component contains some kind of dropdown menu or collapsible part that you want to make sure to be visible when user opens or expands that part.
You can pass a ScrollIntoViewOptions as input of the directive:
active: whether the child component should be in the visible area,first: whether the child component is the first element in the list of elements to be considered.
Example:
<span [sqScrollIntoView]="{active: true}">Some item that is needed to be scrolled into visible area</span>
FocusKeyList and FocusKeyListItem directives
The sqFocusKeyList directive and sqFocusKeyListItem directive are used together
to provide keyboard navigation functionality to items in lists, such as a results list. The sqFocusKeyList directive is added
to the container element and the sqFocusKeyListItem directive is added to each child element. The sqFocusKeyList directive has
the following inputs:
activeItem: the index of the currently active itemwithWrap: a boolean value indicating whether navigation should wrap on the first and last items. The default istrue.
Additionally, sqFocusKeyList raises the itemSelect event with the index of the newly selected item.
Example:
<div class="container" sqFocusKeyList [activeItem]="currentIndex" (itemSelect)="currentIndex = $event">
<div *ngFor="let item of items" class="item" sqFocusKeyListItem>{{item.name}}</div>
</div>
ResizeEvent directive
The sqResize directive uses the native ResizeObserver browser API to generate an event any time the associated element changes size. The new contentRect of the element is passed with the event.
A polyfill is used to emulate this functionality for Internet Explorer.
Example:
<div (sqResize)="onResize($event)"></div>
Sticky Component
The sqSticky component is a container that "sticks" to the top and the bottom of the screen when scrolling. For example, a sidebar containing facets will be always visible on the screen, even when scrolling down a long list of results. Additionally, if the sidebar is itself very long, it will scroll with the content until reaching the bottom of the side bar (and then "stick" to the bottom of the screen). Note that this behavior is not possible when using a simple position: sticky or Bootstrap's sticky-top.
The component accepts as input an object containing the offsets with respect to the top and bottom of the screen. The default value is {top: 0, bottom: 0}.
Note that in Internet Explorer position: sticky is not supported, so the component automatically deactivates its sticky behavior.
Services
UIService
The UIService provides helper methods to listen to screen sizing events and to verify the current screen size to the sizing rules of your component.
There are two event streams that you can subscribe to receive the screen sizing events:
priorityResizeEvent: Observable<UIEvent>This listeners of this stream will be be notified of the resize events first. This may be useful when you want to hierarchize the behavior of your components w.r.t to a resizing event.resizeEvent: Observable<UIEvent>
You can also listen to the resizing of a specific HTML element by adding your listeners with UIService.addElementResizeListener(htmlElement, callback) without bothering about the priority of your listener.
In order to remove a listener added by UIService.addElementResizeListener(), use UIService.removeElementResizeListener(htmlElement, callback).
Then there are a family of methods to compare the current screen size to a screen size in input:
screenSizeIsEqual(screenSize: string): booleanscreenSizeIsGreater(screenSize: string): booleanscreenSizeIsLess(screenSize: string): booleanscreenSizeIsGreaterOrEqual(screenSize: string): booleanscreenSizeIsLessOrEqual(screenSize: string): boolean
In combination with the screen sizing rules represented by the injection token SCREEN_SIZE_RULES, you can design the UI content of your component to be responsive to the size of the application
(cf. Responsive design).
For example, you can decide to replace the display text of a button by its icon if the overall application screen size if less than a given threshold.
public get showButtonText(): boolean {
return this.uiService.screenSizeIsGreaterOrEqual('lg');
}