Auditing applications
In Sinequa, Search-Based Applications can be "audited": User actions (queries, clicks, etc.) are collected and stored server-side to allow admins to study the usage of their applications and the behavior of users. This is a very important process to optimize the search relevance and user experience.
Prerequisites
On the server, several prerequisites are necessary:
-
The creation of an audit index.
-
The creation of jobs to process the audit logs and update the audit index.
-
In the web app's configuration, specify which actions should be collected:
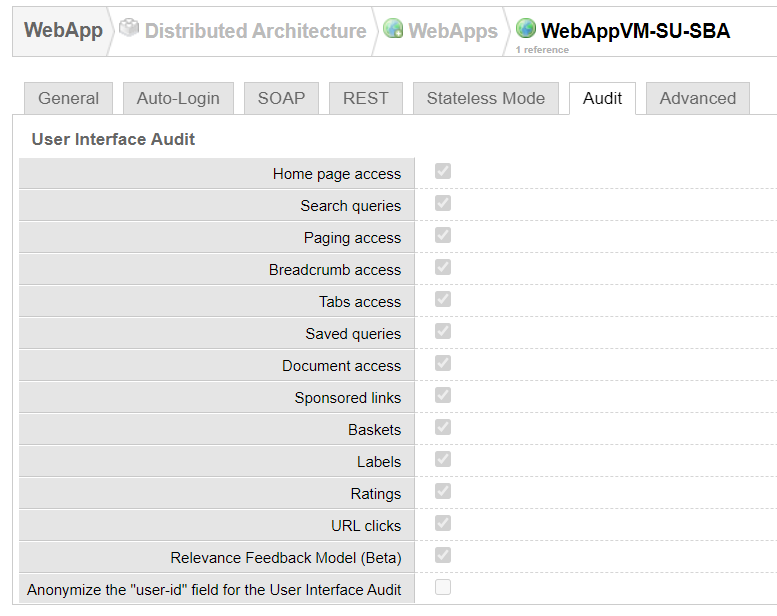
Standard Events
By default, Sinequa components take care of emitting audit events when needed. For example, the SearchService emits events when the user searches for some text and the FacetService emits events when they select a metadata in a facet.
This can happen in two ways:
- Normally, these audit events are emitted by "piggy-backing" on the web service HTTP call corresponding to the audited user action.
- Alternatively, stand-alone audit events can be emitted via the
AuditWebService.
Audit events via standard web service calls
Sinequa Web Services accept an optional $auditRecord parameter that is used to write events to the audit logs.
For example, in the QueryWebService, the web service call looks as follows:
const observable = this.httpClient.post<Results>(this.makeUrl(this.endPoint), {
app: this.appName,
query,
$auditRecord: auditEvents,
queryIntentData
});
Note that the $auditRecord field is supported across all web services, including the custom ones (in particular JsonMethodPlugin).
Audit events via the audit web service
The AuditWebService is a standard Sinequa service that can be injected anywhere in your application to emit "standalone" audit events.
For example, it is used to emit events when users open a document (by following its original URL) in the SearchService:
this.auditService.notifyDocument(
AuditEventType.Click_ResultLink,
record,
results || resultId || "",
{
querytext: this.query.text,
querylang,
},
{
queryhash: results ? results.rfmQueryHash : undefined,
querytext: this.query.text,
querylang: querylang
}
);
Custom Events
Audit events are not limited to a predefined list of event types or a predefined content. It is possible to create new types of events and customize their structure.
The AuditEvent interface is very flexible as it requires:
-
A
type, which can be a standard type (among those listed in theAuditEventType) or a customstring. -
A
detailfield, which is a simple key-value map, where the keys correspond to columns of the audit index (of course, these columns must exist in the audit index schema, which can be customized).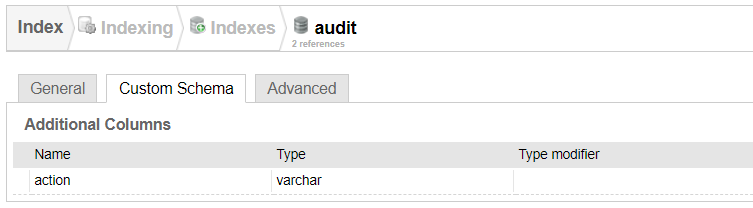
Therefore, emitting a custom standalone event is as simple as the following example:
this.auditWebService.notify({
type: "ResultsView_Change",
detail: {
view: this.resultsViewService.resultsView.name
}
});
Customizing standard events
It is often required to add some custom data to a standard event (or even to all standard events). One solution to that problem would be to modify (or override) the existing services (SearchService, FacetService, etc.), to add the missing data. But this approach is cumbersome and requires more maintenance.
A better alternative is to intercept audit events globally (just before they are sent to the server) and modify them all in this centralized location. This can be achieved by extending the standard AuditInterceptor and overriding the updateAuditRecord() method.
HTTP interceptors are a standard way to manipulate HTTP requests and responses globally in Angular. Sinequa includes an interceptor dedicated to audit events. It is provided by default in application samples, such as Vanilla Search, in the app.module.ts file:
@NgModule({
...,
providers: [
...
// Provides an HttpInterceptor that offers a centralized location through which all client-side
// audit records pass. An application can replace AuditInterceptor with a subclass that overrides
// the updateAuditRecord method to add custom audit information to the records.
{provide: HTTP_INTERCEPTORS, useClass: AuditInterceptor, multi: true},
You can replace this standard interceptor with your custom version:
{provide: HTTP_INTERCEPTORS, useClass: MyAuditInterceptor, multi: true},
This custom interceptor should extend the original version and override the updateAuditRecord() method. In the example below, we modify specifically the Search_Text audit events to include the query web service's name in the detail object.
import { Injectable, Inject } from '@angular/core';
import { AuditInterceptor } from '@sinequa/core/app-utils';
import { AuditRecord, StartConfig, START_CONFIG, AuditEventType } from '@sinequa/core/web-services';
import { SearchService } from '@sinequa/components/search';
@Injectable({
providedIn: "root"
})
export class MyAuditInterceptor extends AuditInterceptor {
constructor(
@Inject(START_CONFIG) startConfig: StartConfig,
public searchService: SearchService){
super(startConfig);
}
protected updateAuditRecord(auditRecord?: AuditRecord) {
auditRecord?.auditEvents?.forEach(event => {
if(event.type === AuditEventType.Search_Text && event.detail) {
event.detail.queryWS = this.searchService.query.name;
}
});
}
}